A fundamental security principle in Cloud Computing is the concept of the Shared Responsibility model. This concept defines the responsibilities of both cloud service providers and customers (Academic institutions, Researchers, Students, etc.) in the well-established cloud service models listed below. In most service models, the cloud service provider is responsible for the lower infrastructure layers, up to the virtualization layer.
For IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), the customer is responsible for the operating system (of the virtual guest machines), the application layers and the data (permissions, auditing, etc.).
For PaaS (Platform as a Service), both the customer and the cloud provider share responsibility over the application layer, and the customer as the data owner is responsible for permissions, auditing, etc.
For SaaS (Software as a Service), which is a fully managed service, the customer is the data owner and responsible for permissions, auditing, etc.
The table below illustrates the various responsibilities of both the cloud provider and the customer:
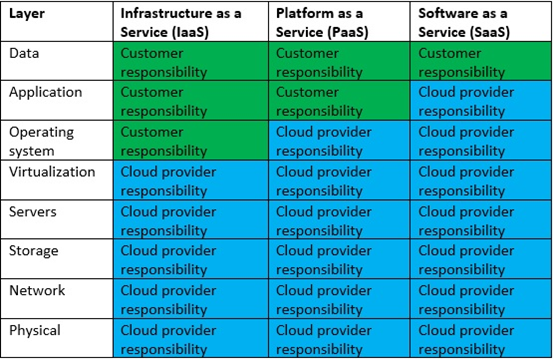
Green: Customer’s responsibility
Blue: Cloud Service Provider’s responsibility
AWS (Amazon Web Services) uses a slightly different shared responsibility model in terms of security. AWS makes a differentiation between the provider (AWS), who is responsible for security of the cloud infrastructure, and the customer (Academic institutions, researchers, students, etc.), who is responsible for security within the customer’s cloud environment.
The diagram below illustrates the various responsibilities of both AWS as the cloud provider and the customer:
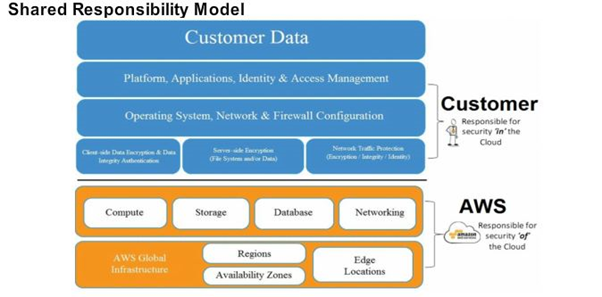
Blue: Customer’s responsibility
Orange: AWS responsibility
Reference:
- https://blog.cloudsecurityalliance.org/2014/11/24/shared-responsibilities-for-security-in-the-cloud-part-1/
- https://blog.cloudsecurityalliance.org/2014/11/25/shared-responsibilities-for-security-in-the-cloud-part-2/
- https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/shared-responsibility-model/
- https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/Shared-Responsibilities-81d0ff91
About the author
Eyal Estrin, cloud architect.
cloud architect.

